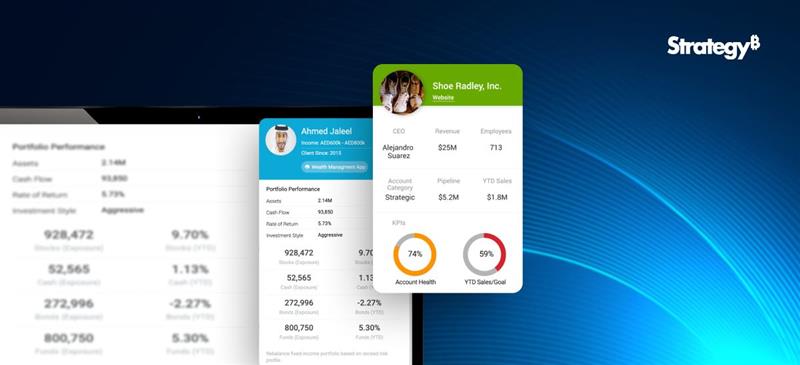
Financial Analytics and Its Importance
Financial analytics offers actionable insights into an organization’s monetary health and performance by utilizing data analysis tools and techniques for analyzing financial data. It involves assessing financial data from diverse sources, like income statements, market data, etc., to identify trends, make strategic, data-driven decisions, and optimize financial operations.
Fundamental finance analytics is critical to businesses as they deliver data-driven insights that equip enterprises to make smarter decisions, optimize operations, and boost profitability. The following aspects imply the significance of financial analytics for businesses.
• Analyzing financial performance
• Creating accurate budgets and plans by forecasting based on market trends and historical data
• Identifying and mitigating financial risks
• Assessing potential investments to make informed decisions
• Analyzing a company’s cost structure for optimization
• Harnessing big data to develop strategies for addressing challenges and making informed decisions
• Facilitating continuous visibility into financial operation and performance
• Detecting data gaps and analyzing historical data to improve business performance
• Preventing fraud and eliminating manual, redundant tasks to enhance efficiency
Tableau for Financial Analytics
Businesses must utilize financial analytics tools and software to improve financial management, comply with regulations, identify cost-efficient prospects, optimize operations, and make informed decisions. These tools automate the analysis and interpretation of financial data, delivering valuable insights into budgeting, forecasting, and performance. Tableau makes financial analytics seamless with powerful, intuitive dashboards that facilitate data-driven decisions. With Tableau, users can easily visualize, analyze, and share data faster and detect patterns and trends that offer actionable insights. Tableau equips enterprises with an in-depth understanding of their spending, enabling effective optimization of resources. Be it tracking capital expenditures or assessing expense spending, Tableau transforms financial data into actionable insights that drive improved business outcomes.
As financial analytics continues to evolve, the future of Tableau in financial analysis looks promising. Amidst the rising intricacies of financial fraud, there is a need for a robust, intuitive platform like Tableau, which is essential to detect fraud faster and reduce the impact of losses. As a popular data visualization and interaction tool in the finance domain, Tableau simplifies raw data, making it interactive and visually intelligible. Tableau uses financial analytics to improve efficiency in the following ways:
• Acquiring insights from the financial data collected from diverse sources
• Predicting accurately by utilizing analytics to get a detailed picture of financial perspectives
• Lowering risk and saving time by tracking accounts to locate inactive or low-activity accounts
Financial Analytics Made Seamless: Tableau’s Robust Capabilities
Tableau empowers financial analysts with deeper insights into financial data, enabling data-driven decisions. Let’s take a look at the distinctive uses of Tableau in finance:
• Automating Data Updates: Unlike traditional data reporting software like Excel, Tableau automates the process of updating data, formulas, and data reports in line with the changes, enabling faster and more efficient financial reporting and allowing users to save significant time.
• Data Visualization: With Tableau’s powerful data visualization capabilities, business giants can easily handle the intricacies of big data through graphical representations, real-time dashboards, and analytical data breakdowns.
• Data Insights: Tableau’s smarter data analytics and insight tools automatically analyze financial data and offer insights into it, allowing effortless analysis of bigger financial datasets for making important financial decisions.
• Financial Reporting: Tableau offers distinctive financial reporting capabilities, transforming traditional reports like P&L statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements into dynamic and automated experiences. Besides, Tableau delivers insightful recommendations based on the analyzed financial data, empowering users to make informed decisions.
• Data Trends and Patterns: With features like data drill-down and data blending, Tableau helps acquire applicable data and identify variations, patterns, or trends within the enterprise.
Tableau in Finance: Key Implementations
As a robust tool for smarter financial analytics, Tableau equips enterprises with the capability to visualize intricate data, enhance operations, and improve the decision-making process. Here are some of the key implementations in Tableau that enhance financial analysis, resulting in insightful scenario analysis and accurate forecasting.
• Developing Interactive Tableau Financial Analysis Dashboards: Tableau dashboards offer a comprehensive view of the financial status of your organization, blending interactive features like action buttons, color schemes, drop-and-down filters, and intuitive layouts. Building engaging dashboards in Tableau converts the static financial data into a visual story, often incorporating various visualizations like dual-axis charts for comparison and bullet graphs for performance metrics. The interactive elements of Tableau dashboards allow for seamless manipulation of data views, enabling users to analyze deeper without switching from the primary dashboard.
Example: Tableau financial analysis dashboards allow tracking key financial metrics like expenses, loan performance, and customer deposits while providing real-time updates.
• Forecasting and Trend Analysis: For businesses to make strategic financial decisions, it is important to foresee future performance. The future of financial forecasting is enhanced by Tableau, which enables the creation of predictive models based on historical data patterns and the integration of statistical forecasting methods to project future trends. It helps businesses understand possible business trajectories.
Example: Tableau creates visualizations comparing past performance against future projections based on historical sales data, seasonal trends, and customer purchase behaviors.
• Scenario Analysis: Tableau facilitates the creation of multiple financial scenarios to assess how various factors affect financial outcomes. Analysts can use Tableau’s flexibility to create different scenarios by modifying input variables to visualize the impacts on financial metrics. It helps stakeholders to have a sound idea of potential risks and opportunities.
Example: Using Tableau to simulate economic conditions helps businesses assess profitability and the impact on non-performing loans (NPLs) and craft mitigation strategies.
• Fraud Detection: Using Tableau for financial analytics helps organizations detect anomalies and suspicious patterns that may imply fraudulent activities. Tableau’s powerful visualization capabilities help detect anomalies in financial transactions, and predictive modeling helps understand potential risks, reduce financial losses, and ensure compliance with security regulations.
Example: Tableau visualizes transaction patterns and anomalies like unusually high spending across different locations.
• Compliance and Risk Management: Tableau helps track financial compliance metrics and identify areas where a business may be at risk of non-compliance with regulations. For instance, it can help visualize tax liabilities, monitor debt covenants, or track audit results. Tableau also provides automated reports that track transactions and regulatory compliance.
Example: A compliance dashboard might track specific ratios indicating whether a company adheres to legal financial limits.
• Expense & Cost Analysis: Organizations can harness Tableau to track and analyze operational costs across departments, locations, or projects. By visualizing cost breakdowns and spending trends, finance teams can identify inefficiencies, optimize budgets, and implement cost-saving strategies.
Example: Tableau visualizes spending trends, helping analyze expenses and detect cost-saving possibilities.
The finance landscape is evolving rapidly, pushing modern businesses to adopt advanced BI solutions like Tableau rather than traditional spreadsheets. It is no longer the era of manual data preparation and analysis. Therefore, most organizations now rely on Tableau to create financial dashboards to track and report KPIs. Being a powerful data visualization platform with advanced analytics and interactive capabilities, Tableau helps build dynamic dashboards and redefine financial analytics. Adopting Tableau for financial services helps organizations harness its innovative features to upgrade their financial data management and reporting processes.